Learn the series of events that led to the Holocaust and related events that occurred during this period..
1933
January 30: Hitler appointed chancellor of Germany.
March 5: Hitler receives strong vote of confidence from German people in Reichstag elections.
March 24: Reichstag gives Hitler power to enact laws on its behalf.
April 7: Jews barred from German civil service.
April 25: Number of Jewish children admitted to German schools and universities reduced.
May 10: Books by Jews and opponents of Nazism burned publicly.
October 19: Germany withdraws from League of Nations.
1934
August 3: Hitler declares himself president and chancellor of the Third Reich after death of Paul von Hindenburg.
1935
January 13: Saar region annexed by Germany.
March 16: Hitler violates Versailles Treaty by renewing compulsory military draft in Germany.
March 17: German army enters Rhineland.
September 15: Nuremberg Laws deprive Jews of German citizenship.
1936
March 3: Jewish doctors no longer permitted to practice in government institutions in Germany.
March 7: Jews no longer have the right to participate in German elections. German army reoccupies Rhineland.
August 1: Olympic Games open in Berlin. Signs reading "Jews Not Welcome" are temporarily removed from most public places by Hitler's orders.
1937
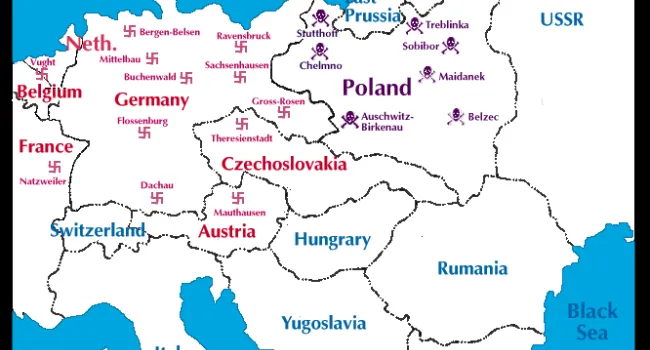
July 16: Buchenwald concentration camp opens.
November 16: Jews can obtain passports for travel outside of Germany only in special cases.
1938
March 13: Austria annexed by Germany.
July 23: German government announces Jews must carry identification cards.
November 7: Attempt made by Herschel Grynszpan to assassinate German diplomat in Paris.
November 9: Kristallnacht, Night of Broken Glass, anti-Jewish riots in Germany and Austria, takes place.
November 12: German Jews ordered to pay one billion Reichsmarks in reparations for damages of Kristallnacht.
November 15: All Jewish children expelled from German schools.
1939
March 15: Germany occupies Czechoslovakia.
August 23: Soviet-German Pact signed.
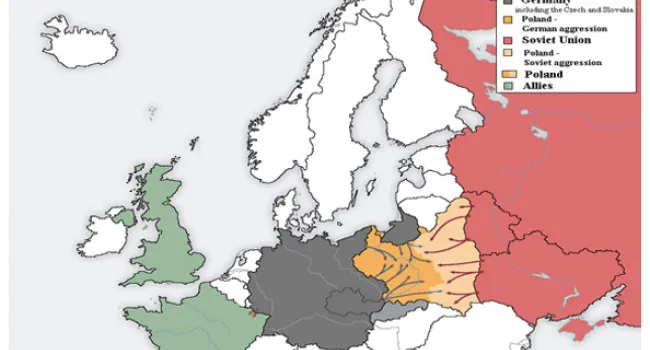
September 7: German army invades Poland. World War II begins.
November 28: First Polish ghetto established.
1940
April 9: German army occupies Denmark and southern Norway.
May 10: Germany invades Holland, Belgium, and France.
June 22: French army surrenders and signs armistice with Germany.
October 3: Anti-Jewish laws passed by Vichy Government in France.
November 15: Warsaw Ghetto closed off approximately 500,000 inhabitants.
November 20: Hungary, Rumania, and Slovakia join the Axis.
1941
May 15: Rumania passes law condemning adult Jews to forced labor.
June: Vichy Government revokes civil rights of French Jews in North Africa.
June 22: Germany invades Soviet Union.
December 8: Chelmno death camp opened near Lodz, Poland.
1942
January 20: Wansee Conference begins.
June 1: Treblinka death camp opens.
July 28: Jewish fighting organization set up in Warsaw Ghetto.
October 4: All Jews still in concentration camps in Germany are sent to death camp at Auschwitz.
1943
April 19: Warsaw Ghetto revolt begins.
June: Nazis order all ghettos in Poland and Soviet Union liquidated.
July 24: Revolt in Italy; Mussolini deposed.
August 2: Armed revolt in Treblinka death camp.
October 2: Order for the expulsion of Danish Jews. Through rescue operations of Danish undergound, 7000 Jews evacuated to Sweden; only 475 people captured by Germans.
October 14: Armed revolt in Sobibor death camp.
1944
March 19: German army invades Hungary.
May 15: Deportation of Hungarian Jews to Auschwitz begins.
June 6: Allied invasion of Normandy.
July 20: Group of German officers attempt to assassinate Hitler.
July 24: Russians liberate Maidanek death camp.
1945
January 17: Evacuation of Auschwitz; prisoners begin death march.
April: Russian army enters Germany from east; Allied army enters from the west.
April 30: Hitler commits suicide.
May 8: Germany surrenders.
November: Nuremberg Trials begin.
1962
December: Adolf Eichmann executed in Israel.
1965
February: Legislation passed in Germany to allow prosecution of Nazi war criminals to be extended for additional 20-year-period.
1987
May: Klaus Barbie trial begins in Lyons, France.
Standards
- 7-4 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the causes and effects of world conflicts in the first half of the twentieth century.
- The influence of both world wars and the worldwide Great Depression are still evident. To understand the effects these events had on the modern world, the student will utilize the knowledge and skills set forth in the following indicators:
- 7-4.5 Summarize the causes and course of World War II, including drives for empire, appeasement and isolationism, the invasion of Poland, the Battle of Britain, the invasion of the Soviet Union, the "Final Solution," the Lend-Lease program, Pearl Harbo...
- 7-4.6 Analyze the Holocaust and its impact on European society and Jewish culture, including Nazi policies to eliminate the Jews and other minorities, the Nuremberg trials, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the rise of nationalism in Southwest...
- The influence of both world wars and the worldwide Great Depression are still evident. To understand the effects these events had on the modern world, the student will utilize the knowledge and skills set forth in the following indicators:
- USHC-7 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the impact of World War II on the United States and the nation’s subsequent role in the world.